
Educational Resources
This is a resource library of educational resources on dementia. There’s so much information out there and it’s hard to know what to trust. These resources have been reviewed by local subject matter experts and added to this searchable and filterable library for your convenience.
Much thanks to Dr. Kevin Kawamoto, the University of Hawai’i Center on Aging, and the Workforce Development workgroup members for putting together this Master Curriculum. The curriculum was designed with an “a la carte” model in mind, allowing educators and trainers to choose which items would be most suitable and appropriate for their particular audiences. Click here for the full document or scroll down to search for the topic you’d like to learn about.
Resource Library
10 Early Signs and Symptoms of Alzheimer’s
- Type: Early Detection
- Prevention Level: Secondary
- Material Type: Literature
-
Source:
Alzheimer’s Association
10 Warning Signs of Alzheimer’s Disease
- Type: Early Detection
- Prevention Level: Secondary
- Material Type: Literature
-
Source:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
10 Ways to Love Your Brain
- Type: Brain Health and Prevention
- Prevention Level: Primary
- Material Type: Literature
-
Source:
Alzheimer’s Association
A Few Words from Harvey and William, Two Alzheimer’s Patients.
Description from YouTube: “The challenges of Alzheimer’s Disease for both the patient and caregiver.” (3 minutes, 21 seconds)
- Type: Case Studies
- Prevention Level: Tertiary
- Material Type: Video
-
Source:
Johnson & Johnson
A Guide to Psychosocial Interventions in the Early Stages of Dementia
- Type: Psychosocial Interventions
- Prevention Level: Tertiary
- Material Type: Literature
-
Source:
The British Psychological Society
Prevention Levels
The three points of prevention, as defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), are:
Primary Prevention
Primary Prevention — or risk reduction — strives to intervene before health effects occur, through measures such as promoting healthy and safe behaviors (e.g., eating well, exercising regularly, not smoking), mandating safe and healthy practices (e.g., use of seatbelts and bike helmets), and limiting exposure to factors associated with a disease or health condition (e.g., asbestos, lead and mercury).
Secondary Prevention
Secondary Prevention — or early detection and diagnosis — aims to identify diseases in the earliest stages, before the onset of more severe symptoms (e.g., increasing awareness of symptoms, promoting early diagnosis and educating health care providers about the benefits of early diagnosis and intervention strategies).
Tertiary Prevention
Tertiary Prevention — or management of comorbidities — involves managing disease post diagnosis to minimize negative health and quality of life effects. Comorbidities occur when a person has more than one disease or condition at the same time. Tertiary prevention is also important when thinking about caregivers, who are influential in managing care and reducing complications, sometimes at the expense of their own health.
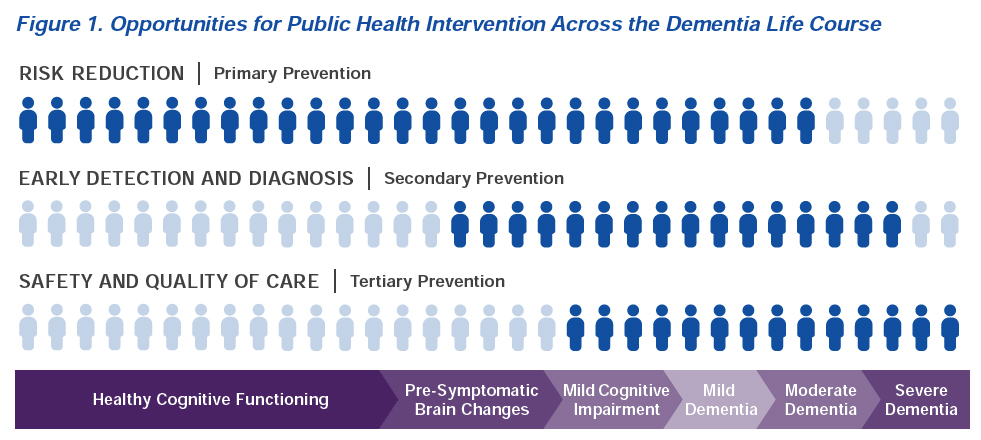
“There are opportunities for public health intervention across the dementia life course. The public health community can intervene across the points of prevention — primary, secondary and tertiary — to impact the brain health of the population. The figure shows the potential impact of the different prevention points throughout the continuum of dementia.
Public health action is critical to reduce the risk of mild cognitive impairment, improve access to early detection and diagnosis and improve the safety and quality of care for people living with dementia… In early life and throughout the life course, primary prevention can make a difference in sustaining cognitive function across a population.” For those with Mild Cognitive Impairment, “secondary prevention in the form of early detection and diagnosis is paramount.” “Tertiary prevention strategies can connect the person living with dementia to treatment and support services to help preserve their independence and quality of life for as long as possible.”
– Healthy Brain Initiative: State and Local Road Map for Public Health, 2023-2027
Resources on Dementia for Children
Witnessing a loved one going through changes associated with dementia can be confusing, scary, and alienating for a child, especially when adults don’t effectively communicate what’s going on.
Dr. Kevin Kawamoto compiled a list of children’s book titles with descriptions provided on Amazon.com so that adults can review possible materials that would be suitable for helping to start a conversation with their keiki about dementia.
Learn MoreSupport Groups & Upcoming Events
Learn ways to communicate effectively with people living with dementia. This session will be led by expert local trainer, Dorothy Colby, Certified Positive Approach to Care.
Sign Up for Our Email Newsletter
Receive News, Alerts & Updates via Email



Follow Us on Social Media